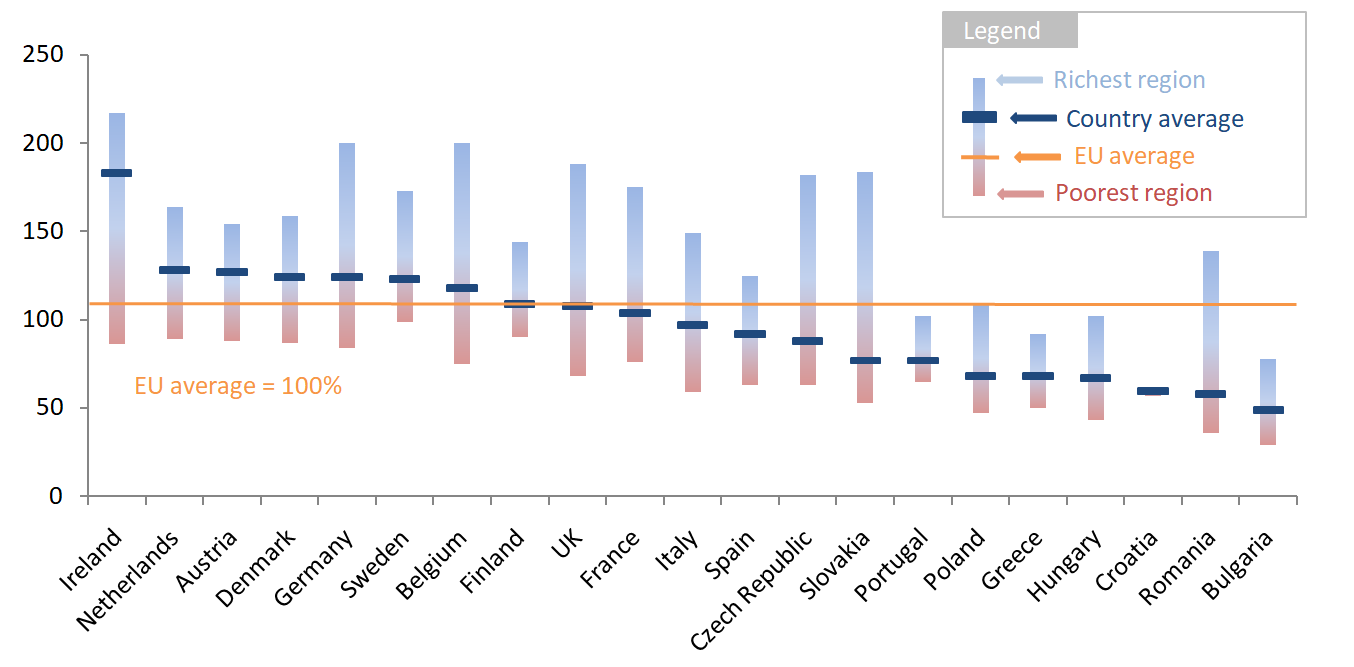
Unemployment in 2017: A Regional Review
In 2017, the labor market in Bulgaria continued its expansion and the improvement discussed in recent years is increasingly visible at the regional level.
Yavor Alexiev
In 2017 the Bulgarian labour market continued its expansion, and the improvement that took place in the last couple of years is becoming more visible on the regional level. According to the last annual data provided by the Employment agency (EA) there are 30 municipalities with unemployment below 5% (marked blue on the map) and 80 more with unemployment between 5 and 10 per cent. In 2013, in the heat of the labour market crisis the number of municipalities with such levels of unemployment were 3 and 43, respectively. Compact groups of low unemployment municipalities can be found in North Bulgaria, around Varna, as well as in the area around Troyan, Gabrovo and VelikoTarnovo, and in the South – around the capital, Plovdiv, Pazardzik, Burgas, Stara Zagora and Kazanlak.
Unemployment in the Bulgarian municipalities (2017 compared to 2013)

Source: EA, IME calculations
Municipal level data
Compared to 2016, unemployment has increased only in 4 municipalities – Brezovo (+6 percentage points), Bobovdol (+2.8 pr.p.), Lisichovo (+0.8 pr.p.) and Tryavna (+0.2 pr.p.). Despite the overall improvement, compact clusters of municipalities with high levels of unemployment (above 25%) still remain. A large part of North Bulgaria is still in the red, which is also true for the mixed-ethnicity regions as well as most municipalities along the Danube. In most cases, municipalities with high unemployment are either very far from the leading economic centres and the traditional flows of daily labour commuting, or have very low levels of education and training of the labour force. This combination of negative factors does provide for a near-future solution of their problems; it is more likely that the opposite is true, as the negligibly small effect of the overall economic growth on their local labour markets points to a long-term isolation from the processes taking place on the national level.
EA data also show that:
- Vidin is the only district centre where unemployment is still above 10% in 2017. Unemployment above 5% in North Bulgaria is observed in all North-Western district centres, as well as in Razgrad, Targovishte and Silistra;
- In South Bulgaria there are only four district centres with unemployment above 5% - Blagoevrgad (6.2%), Sliven (9.6%), Karzdali (5.8%) and Smolyan (6.3%);
- Most of the tourist municipalities achieve very good results – in 2017, unemployment in Bansko, Primorsko and Nesebar was below 5%, in Pomorie, Sozopol, Razlog and Chepelare – below 10%;
- Relatively low levels of unemployment are observed also in municipalities with large companies, such as Panagyurishte (7.3%), Etropole (7.8%) and Sopot (2.6%).
Structural issues
While the data provided by EA undoubtedly provides reason for optimism, some negative long-term trends can also be observed. The primary market in many districts still has difficulty providing such a number of workplaces as necessary to reduce unemployment faster and in a more noticeable way.
In addition, 2017 EA data for the characteristics of the unemployed show that:
- 54.6% of the unemployed have no training and this share (available only on the district level) is the highest in Sliven (75.8%), Shumen (71.7%) andPazardzik (66.6%) and the lowest in the capital (23.4%), Gabrovo (28.2%) andPernik (40.2%);
- 27.8% of the unemployed have basic or no education, and this share is the highest in Sliven (52.7%), Shumen (44.2%) andYambol (43.8%), thelowest – inthe capital (4.4%), Gabrovo (6.7%) andSmolyan (11.3%);
- Unemployed for more than a year were 37% of registered in the labour offices, which is 4,5 percentage points below than the 2016 level. The most significant drop in long-term unemployment is in Gabrovo and Plovdiv, where the 2017 levels are respectively 17.3% and 28.3%. There are, however, districts where the relative share of the long-term unemployed is growing, and it reached 58% in Vidin, 56% in Montana and 48% in Silistra.
Following the above data, the claims that the labour offered in the economy does not meet the requirements of employers are far from surprising. In order to solve this issue, in the past months the government introduced changes aiming to reduce red tape in the process of hiring foreign workers – an important measure in support of the continued expansion of the labour market. The problems with the nature and quality of the active labour market policies however remains, as in 2018 the state continues to rely on subsidized labour rather than unemployed retraining and education. In addition, the effect of the record increase of the minimum wage on the poorest regions is yet to be assessed, and it appears that the debate around the mechanism for the setting of the minimum wage has died out.